What is the difference between vibration welding and hot plate welding?
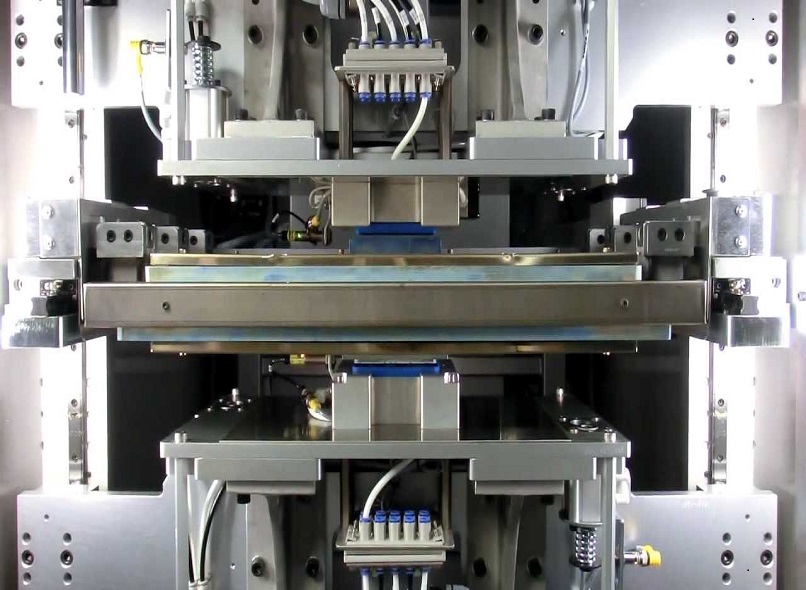
Vibration welding and hot plate welding are both commonly used techniques in the field of plastic welding. However, there are distinct differences between the two methods.
Vibration welding is a process where two plastic parts are joined together by applying frictional heat and pressure. The process involves oscillating one of the parts at a high frequency against the other part, causing frictional heat to build up. As the heat softens the plastic, pressure is applied to fuse the two parts together. Vibration welding is particularly effective for joining large plastic parts or parts with complex geometries. It offers several advantages, such as minimal part deformation, fast cycle times, and the ability to weld dissimilar materials. The high-frequency vibrations create molecular friction, ensuring a strong bond between the parts. Additionally, the process allows for precise control over the welding parameters, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
On the other hand, hot plate welding involves heating a metal plate to a specific temperature and pressing it against the two plastic parts to be joined. The heat from the plate softens the plastic, and once the desired temperature is reached, the plate is removed, and the two parts are pressed together under pressure. As the plastic cools down, it solidifies, creating a strong bond between the parts. Hot plate welding is commonly used for joining thermoplastics with high melting points or for parts that require a large surface area for joining. It offers advantages such as consistent temperature control, ease of use, and the ability to weld large parts with uniform heating. The process is often used in industries such as automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and packaging.
In addition to their differences, there are also some similarities between vibration welding and hot plate welding. Both techniques require the plastic parts to be properly prepared, with clean and flat surfaces for optimal bonding. They also require precise control over the welding parameters to ensure a successful weld. Both methods can produce strong and reliable joints when executed correctly, providing excellent mechanical strength and hermetic seals.
When considering which method to use, several factors should be taken into account. The size and complexity of the parts, the type of plastic being welded, the desired strength of the joint, and the production requirements all play a role in the decision-making process. Vibration welding is advantageous for larger and more complex parts, while hot plate welding excels in joining thermoplastics with high melting points or for applications that require a large surface area for bonding.
It is worth noting that there are variations and advancements in both vibration welding and hot plate welding techniques. For example, in vibration welding, ultrasonic vibration welding is a variation that uses higher frequencies for more precise control and faster welding times. In hot plate welding, infrared heating can be used as an alternative to traditional metal plates, offering advantages such as reduced cycle times and energy efficiency.
In conclusion, vibration welding and hot plate welding are two distinct techniques used in plastic welding, each with its own advantages and applications. Vibration welding relies on oscillating frictional heat and pressure, while hot plate welding utilizes a heated metal plate and pressure. Both methods offer reliable and strong bonding capabilities, but the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the project. Understanding the differences between these techniques allows for informed decision-making and ensures the successful joining of plastic parts in various industries.





