Unveiling the Standard Hot Plate Welding Process
Welcome to our comprehensive guide about hot plate welding! Hot plate plastic welding is a versatile, precise, and efficient method used in plastic welding. In this guide, we will explore the standard hot plate welding process, its various types, its wide-ranging applications, and the advantages that make it a staple in industries worldwide.
The Essence of Hot Plate Welding
Hot plate plastic welding, also known as heated platen welding, is a thermal welding process mainly employed to join thermoplastic materials. This technique uses heat and pressure to create strong, hermetic seals in plastic components.
Key Components of a Hot Plate Welding System
Before we dive deeper into the standard hot plate welding process, let's familiarize ourselves with the essential components that make up a hot plate plastic welding system:
- Hot Plate or Heated Platen: The hot plate is the central element of the system, typically made of a thermally conductive material like aluminum or steel. It is heated to the desired temperature, and its flat surface ensures even heat distribution across the interface of the plastic parts.
- Fixturing: Fixturing refers to the tooling and fixtures used to hold the plastic components securely in place during the welding process. Proper alignment is critical to ensure precise welding.
- Pressure System: A pressure system is employed to apply force to the plastic components during the welding operation. This pressure helps in achieving intimate contact between the parts, promoting uniform melting and bonding.
- Temperature Control: Precise temperature control is a cornerstone of hot plate welding. Temperature controllers regulate the hot plate's temperature to ensure it reaches and maintains the optimal welding temperature for the chosen plastic materials.
The Standard Hot Plate Welding Process
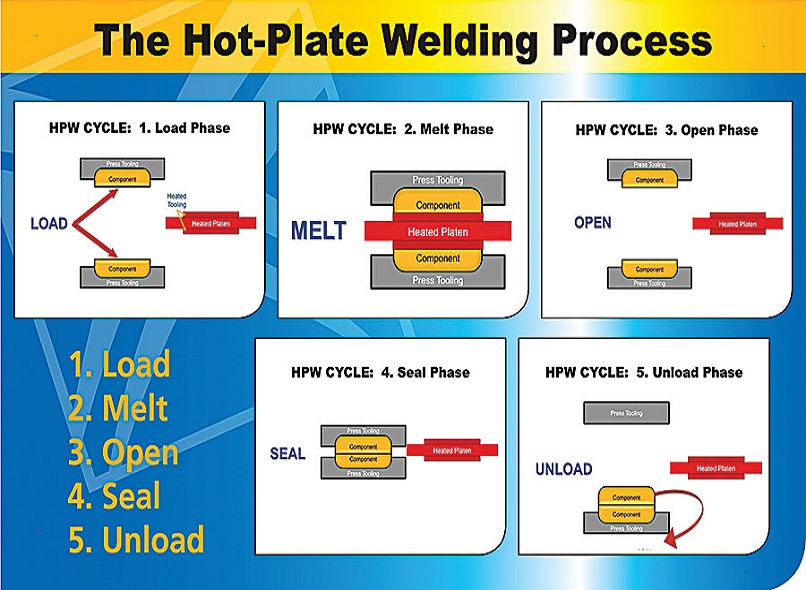
Now, let's dive into the step-by-step process of standard hot plate plastic welding:
1. Material Preparation: The first step is to prepare the plastic components to be joined carefully. This includes ensuring that the surfaces to be bonded are clean, free from contaminants, and properly aligned within the fixtures.
2. Clamping: The prepared plastic parts are securely clamped into the fixtures, ensuring that they are in precise alignment with one another.
3. Heating the Platen: The hot plate is heated to the appropriate temperature for the chosen plastic materials. This temperature is typically just below the melting point of the plastics.
4. Contact and Softening: Once the hot plate reaches the desired temperature, the plastic components are brought into contact with the heated platen. The heat from the platen softens the plastic at the interface, causing it to become pliable and molten.
5. Application of Pressure: As the plastic materials soften, pressure is applied to the components, pressing them together with a controlled force. This pressure ensures that the molten plastic spreads evenly, promoting a strong and uniform bond.
6. Welding Time: The duration of the welding cycle, often referred to as "welding time," is carefully controlled. This time is based on the type and thickness of the plastic materials being joined. During this period, the molten plastics meld together and create a solid-state bond.
7. Cooling and Solidification: After the welding time elapses, the pressure is maintained briefly to allow the plastics to cool and solidify. The solidification phase ensures that the bond is robust and fully formed.
8. Release and Inspection: Once the joint has solidified, the clamping pressure is released, and the welded assembly can be removed from the fixtures. The joint is inspected for quality, integrity, and hermeticity to ensure it meets the desired standards.
Types of Hot Plate Welding
Hot plate welding comes in several variations to accommodate diverse applications and materials. Let's explore some of the common types:
- Standard Hot Plate Plastic Welding: Standard hot plate welding, as described above, is the most common type. It is suitable for a wide range of thermoplastic materials and is used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
- Vibration Hot Plate Plastic Welding: Vibration hot plate welding introduces an oscillatory motion to the plastic parts in contact with the heated platen. This motion enhances heat distribution and material flow, resulting in faster welding times and improved joint quality. Vibration hot plate welding is often used for larger or complex parts.
- Infrared Hot Plate Plastic Welding: Infrared hot plate welding employs infrared radiation to heat the plastic materials instead of direct contact with a heated platen. This method is particularly useful for materials with high heat sensitivity and can achieve faster welding times.
- Hot Gas Hot Plate Plastic Welding: Hot gas hot plate welding combines hot plate welding with the introduction of hot gas to heat the plastic materials. It is suitable for joining materials with different melting points or dissimilar materials.
- Hot Melt Extrusion Plastic Welding: Hot melt extrusion welding is a variant that involves extruding molten plastic material onto one of the parts to be joined. The parts are then pressed together while the extruded material is still in a molten state. This method is often used for large and complex components.
Applications of Standard Hot Plate Welding
Standard hot plate welding finds widespread application across various industries, owing to its versatility and ability to create strong, reliable joints. Here are some notable applications:
1. Automotive Industry: Hot plate welding is extensively used in the automotive sector for joining plastic components such as bumpers, dashboard assemblies, air intake systems, and fuel tanks. The technique provides strong, leak-proof seals and helps reduce vehicle weight.
2. Medical Devices: Hot plate welding is employed in the manufacture of medical devices, including IV components, blood filters, and respiratory equipment. It ensures hermetic seals and sterilizability, crucial in the medical field.
3. Aerospace: The aerospace industry relies on hot plate welding for components such as ducting systems, interior panels, and various structural parts. The technique's ability to create lightweight yet robust bonds is advantageous in aerospace applications.
4. Consumer Goods: Hot plate plastic welding is used in the production of consumer goods like water filters, household appliances, and toys. It provides an aesthetically pleasing finish and enhances product durability.
5. Electrical and Electronics: Many electrical and electronic products utilize hot plate plastic welding for components such as connectors, switches, and housings. The process creates secure and moisture-resistant seals.
6. Packaging: The packaging industry benefits from hot plate welding for creating airtight and tamper-evident seals in plastic packaging materials.
Advantages of Standard Hot Plate Welding
Standard hot plate plastic welding offers several advantages that make it a preferred choice in many manufacturing processes:
- Versatility: Hot plate plastic welding is compatible with a wide range of thermoplastic materials, making it suitable for diverse applications.
- Precise Control: The process allows for precise control over temperature, pressure, and welding time, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
- Strong Bonds: Hot plate welding creates strong and hermetic bonds that are resistant to leaks and environmental factors.
- Minimal Material Distortion: Since the process operates below the plastic's melting point, there is minimal material distortion or warping.
- Clean and Efficient: Hot plate welding is a clean and energy-efficient process, with minimal waste generated.
- Scalability: The process can be adapted for both small and large-scale production, making it suitable for various industries.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading our comprehensive guide about hot plate welding! We hope this guide has given you a better understanding of the standard hot plate welding process, its various types, and its wide-ranging applications. Hot plate welding is an essential tool in many industries worldwide, offering versatility, precision, and efficiency in plastic welding. As technology continues to advance, hot plate welding is likely to become even more versatile and accessible in the future. Its ability to produce high-quality, reliable bonds while maintaining material integrity makes it an indispensable tool in the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing and fabrication. We look forward to seeing how hot plate welding continues to shape the way we design and assemble plastic components, driving innovation across a multitude of industries.





