How Does the Ultrasonic Generator Work?
An ultrasonic generator is an electronic device that produces high-frequency signals that are converted into sound waves by a transducer. These sound waves have a frequency that is higher than the upper limit of human hearing, usually above 20 kHz, hence the term "ultrasonic". Ultrasonic generators are used in a variety of applications, including cleaning, welding, medical imaging, and more.
The Basics of Ultrasonic Technology
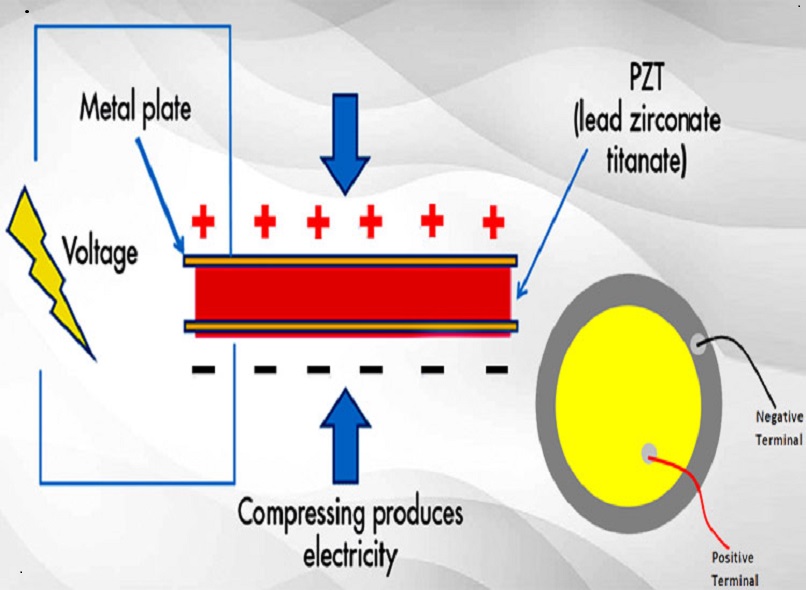
Ultrasonic technology is based on the concept of mechanical vibrations. When an alternating current is applied to the piezoelectric transducer of an ultrasonic generator, it creates a mechanical vibration that is transmitted through a medium, such as air or water. The vibration results in the creation of sound waves that can be used for various applications.
The frequency of the sound waves produced by the ultrasonic generator is determined by the frequency of the electrical signals generated by the generator. The frequency of the sound waves can be adjusted by changing the frequency of the electrical signals, which can range from a few kilohertz to several megahertz.
Applications of Ultrasonic Generators
One of the most common uses of ultrasonic generators is in cleaning applications. Ultrasonic cleaning uses high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic bubbles in a cleaning solution. These bubbles then collapse, creating a scrubbing action that cleans the surface being cleaned. Ultrasonic cleaning is an effective and efficient method of cleaning, as the bubbles can penetrate even the smallest crevices and hard-to-reach areas. This makes ultrasonic cleaning ideal for cleaning items such as jewelry, firearms, and medical instruments.
Ultrasonic generators are also used in welding applications. Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency sound waves to create friction heat, which melts and fuses two materials together. This method of welding is commonly used in the automotive industry to join plastic parts together.
In medical imaging, ultrasonic generators are used to produce high-frequency sound waves that are transmitted into the body. These waves bounce off internal organs and tissues, creating an image that can be used for diagnostic purposes. This method of imaging is known as ultrasound, and it is commonly used to examine the heart, liver, and other organs.
Other applications of ultrasonic generators include sonochemistry, where high-frequency sound waves are used to create chemical reactions, and ultrasonic cutting, where high-frequency sound waves are used to cut materials such as rubber, plastics, and foods.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Generators
Ultrasonic generators offer several advantages over other types of generators. They are more efficient, as they require less energy to produce high-frequency sound waves. They are also more precise, as the frequency of the sound waves can be controlled and adjusted. This makes ultrasonic generators ideal for applications where precision is important, such as medical imaging and cleaning.
Ultrasonic generators are an essential tool in many industries, providing a way to create high-frequency sound waves for a variety of applications. By understanding how ultrasonic generators work, we can appreciate the role they play in our daily lives and the many ways they make our world a better place. Ultrasonic technology has come a long way since its inception and continues to evolve, offering new possibilities for a wide range of industries.





