What materials are used in vibration welding?
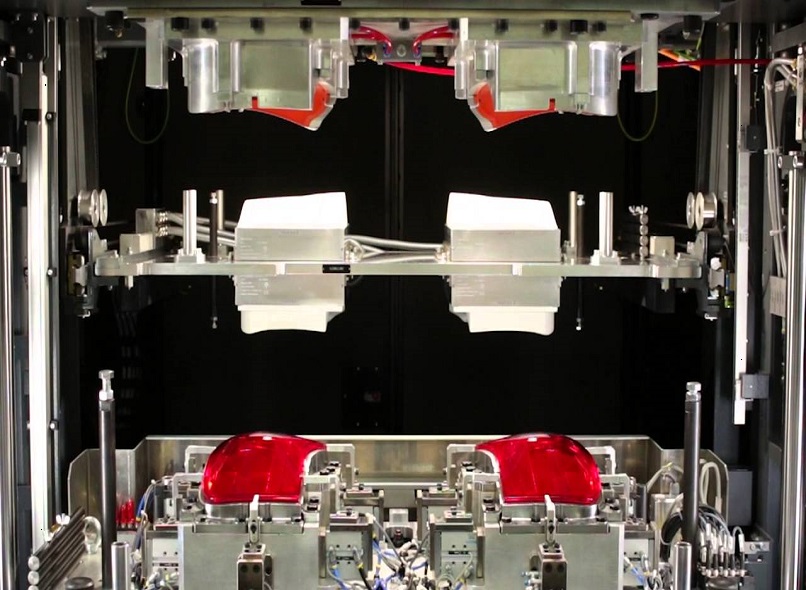
Vibration welding, a widely employed technique for joining thermoplastic materials, relies on the use of specific materials that can effectively bond under high-frequency vibrations. The selection of appropriate materials is crucial to ensure strong and durable welds. Let's delve deeper into the materials commonly used in vibration welding:
- Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer that offers excellent chemical resistance, low cost, and high strength. It is widely used in industries such as automotive, packaging, and appliances. PP is particularly suitable for vibration welding due to its compatibility with other materials and its ability to create strong and reliable welds.
- Polyethylene (PE): PE is another widely utilized material in vibration welding. It is known for its flexibility, impact resistance, and resistance to environmental stress cracking. PE is commonly employed in applications such as pipe fittings, containers, and automotive components.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Polycarbonate is a durable and transparent material with exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity. It is often chosen for vibration welding applications that require strength, transparency, and impact resistance, such as automotive lighting and electronic enclosures.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a versatile thermoplastic that combines the strength and rigidity of acrylonitrile and styrene with the toughness of polybutadiene. It is widely used in industries such as automotive, appliances, and consumer goods. ABS exhibits good vibration welding characteristics and is commonly used for joining parts with complex geometries.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): PVC is a popular choice for vibration welding applications where chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties are essential. It is extensively employed in construction, plumbing, and electrical industries. PVC offers good weldability and is compatible with various other thermoplastics.
- Polyamide (PA): Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is a thermoplastic material that boasts excellent mechanical properties, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. It finds applications in industries such as automotive, electronics, and textile manufacturing. PA exhibits good vibration welding characteristics and is suitable for joining parts that require high strength and dimensional stability.
These materials represent just a fraction of the options available for vibration welding. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application, including mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and environmental factors. It is essential to consider factors such as melting temperature, surface quality, and compatibility when selecting materials for vibration welding. Conducting thorough compatibility testing and consulting material suppliers can help ensure successful and robust welds.





